Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells (DSSCs); Understanding and Optimizing Energy and Electron Transfers Throu
Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells (DSSCs); Understanding and Optimizing Energy and Electron Transfers Through Transient Absorption Data
Introduction to DSSCS
The Sun, whose light energy hitting Earth is
several times greater than the global need, has become a growing source of
green energy production with hopes of decreasing the amount of fossil fuels
burned. However, current solar panels based on silicon require high cost
material processing techniques and can contain caustic materials. The
development of next generation solar fuel sources, based on dye sensitization
and subsequent energy and electron transfers to drive current, or hydrogen
production and water oxidation, will rely on understanding the fundamental
photophysical properties of the dyes and their device constructs. The Edinburgh
Instruments LP980 Transient Absorption Spectrometer is the world’s only commercial
system capable of making time-gated spectral transient measurements with an
ICCD detector and kinetic lifetime traces from nanoseconds to seconds to fully
understand the photoinduced energy and electron transfers associated with
Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells (DSSCs).

Figure 1:
The Edinburgh Instruments LP980 Spectrometer
Research
Researchers at Florida State
University, under Prof. Kenneth Hanson, have utilized an L980 spectrometer to
study the energy and electron transfer characteristics of a self-assembled DSSC
on TiO2. The bilayers contain two complimentary dyes to maximize light absorption,
facilitate efficient, directional energy/electron transfer, and minimize
unwanted recombination (ACS
Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 28633-28640).
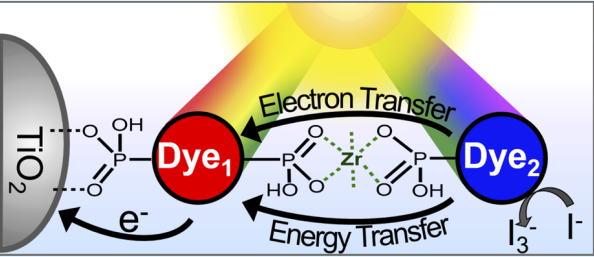
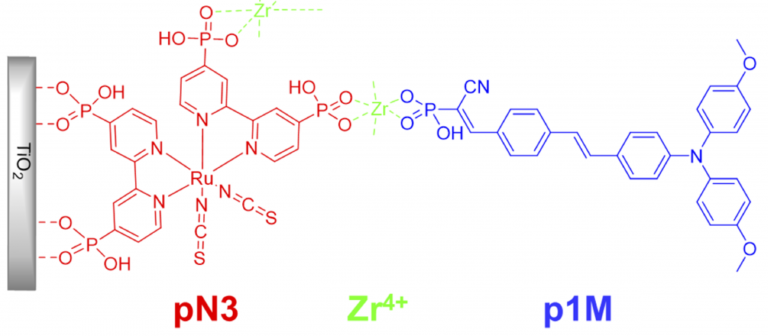
Figure 2:
Multi-layer, self-assembled DSSC construct studied by Prof. Hanson and his team
at Florida State University.
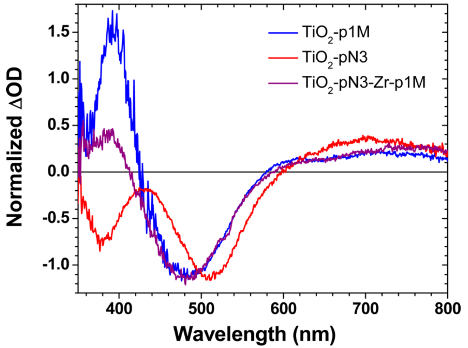
Figure 3: Photo-induced transient absorption spectra of the individual dyes attached to TiO2, and the self-assembled, bilayer DSSC construct 10 ns after laser excitation (laser exc. = 532 nm).
The defined spectral features in the transient
absorption of each individual dye (Figure 3) shows that upon photoexcitation,
each dye undergoes electron transfer to the TiO2. In the bilayer system, the
spectra resemble that of p1M+; consistent with intermolecular energy and
electron transfer as well as interfacial electron transfer as depicted in
Figure 4.
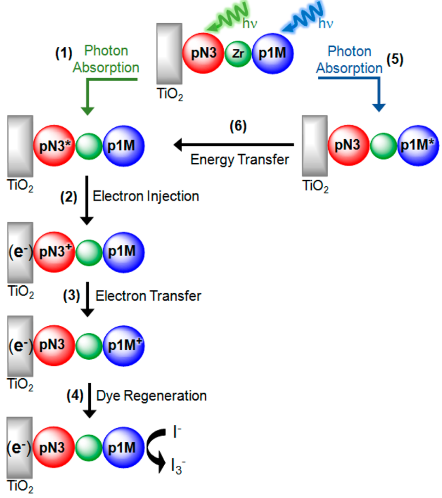
Figure
4: The proposed energy and electron transfer events in a novel
bilayer, self-assembled DSSC with an increased efficiency relative to the
single dye based DSSCs.
Conclusion
Utilizing bilayer DSSCs that are designed to maximize energy and electron transfers rates and minimize unwanted recombination were shown to increase solar energy conversion efficiencies by more than 10% relative to their single dye constructs. Photoinduced energy and electron transfer intermediates were recorded by an Edinburgh Instruments LP980 Transient Absorption Spectrometer. This enabled the structure-function relationship in this novel material whose properties can be translated into devices for solar energy production.
The LP980 for DSSCS Research
If you are working in the field of DSSCS, why not get in touch to find out how the LP980 can be used to help you with your research.
For more information on LP980 Flash Photolysis, please visit Edinburgh Instrument website: https://www.edinst.com
