Home· · ·Techcomp college· · ·Maintenance Center
Maintenance Center
Amino Acid Analyzer Basic Course
1. Principle and basics of amino acid analysis
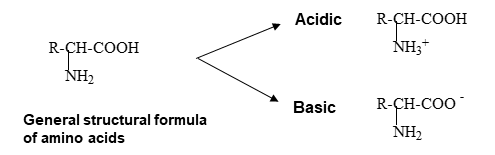
Generally, organic compounds having -COOH (carboxyl group) and -NH 2 (amino group) in the molecular structure are called amino acids.
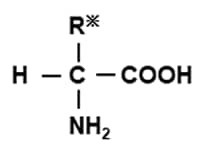
Fig. 1 General structural formula of amino acids
Individual organic groups are bonded to R. Characteristics of each amino acid differ depending on the nature of R.
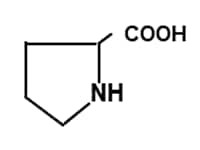
Fig. 2 Structure of Proline (Pro)
Proline has a ring structure. It shows specific optical properties different from other amino acids.
Amino acids are represented by three-letter code that are almost unified worldwide.
Table 1 Three-letter codes of amino acids
|
Asp |
Aspartic acid |
Val |
Valine |
|
Thr |
Threonine |
Met |
Methionine |
|
Ser |
Serine |
Ile |
Isoleucine |
|
Asn |
Aspargine |
Leu |
Leucine |
|
Glu |
Glutamic acid |
Tyr |
Tyrosine |
|
Gln |
Glutamine |
Phe |
Phenylalanine |
|
Pro |
Proline |
Lys |
Lysine |
|
Gly |
Glycine |
His |
Histidine |
|
Ala |
Alanine |
Trp |
Tryptophan |
|
Cys |
Cystine |
Arg |
Arginine |
In the field of amino acid analysis, Asparagine (Asn) and Glutamine (Gln) may be written as AspNH2 and GluNH2. Similarly, Cys may refer to Cysteine.
1)
Standard amino acids (protein hydrolyzate amino acids)
The proteins that make up all animals are composed of amino acids. Amino acids
that make up the proteins are called standard amino acids (protein hydrolyzate
amino acids). As of today, 20 standard amino acids have been identified.
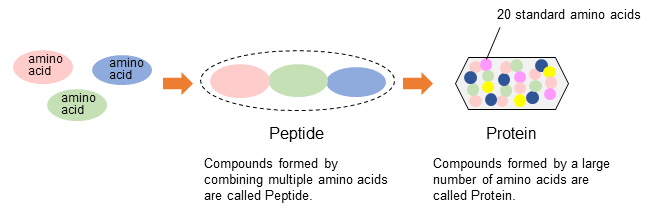
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of amino acids, peptides, and proteins
2)
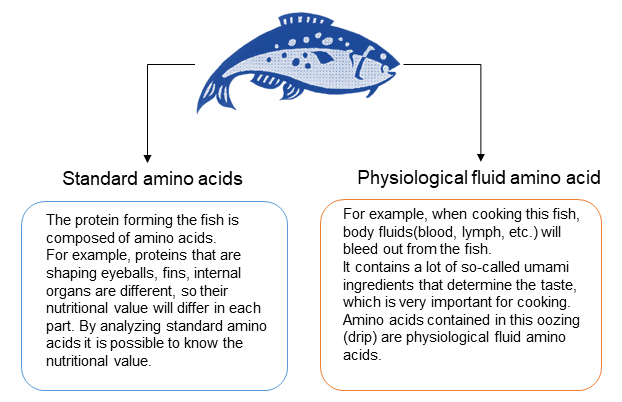
Physiological fluid amino acids (free amino acids)
Basic of amino acids are 20 standard amino acids mentioned above, but if you
take in them as food, it will be digested and will change to various
substances. These amino acids including metabolites and precursors are called
physiological fluid amino acids (free amino acids). Approximately 40
physiological fluid amino acids have been identified.
2. Method for analyzing amino acids
Most of amino acids are difficult to separate and detect because their hydrophilicity is high, and their UV absorption and fluorescence are low. With the post-column ninhydrin method, the Hitachi LA8080 Amino Acid Analyzer can afford separation and analysis of approximately 50 amino acids.
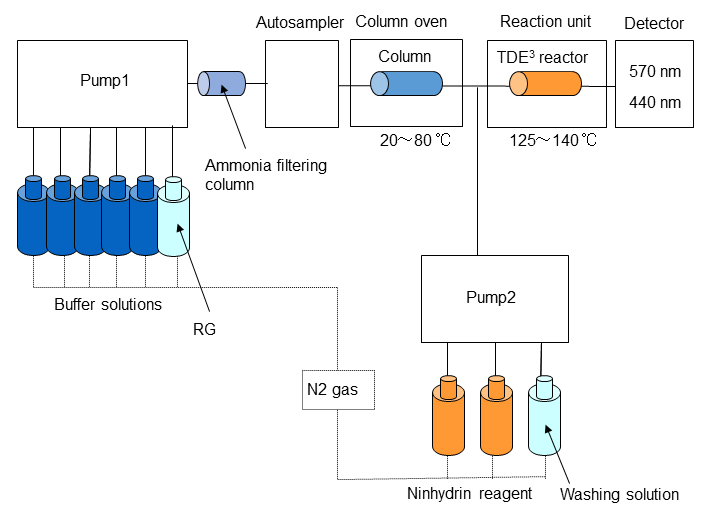
Fig. 4 Flow Diagram of LA8080
2-1. Cation exchange column and separation of amino acids
1. Amino acids are charged to + in the acidic solution, and electric attraction is generated again cation exchange resin.
2. In contrast, amino acids
are charged to - in the basic solution, so that they repel and pass through the
cation exchange resin.
(Utilizing this chemical property, we use a sodium hydroxide solution (basic
solution) for washing out residual substances in the column after analysis. It
is called regeneration (RG) process.)
3. In amino acid analysis, separation is carried out by changing the pH of the eluent from acidic to basic.
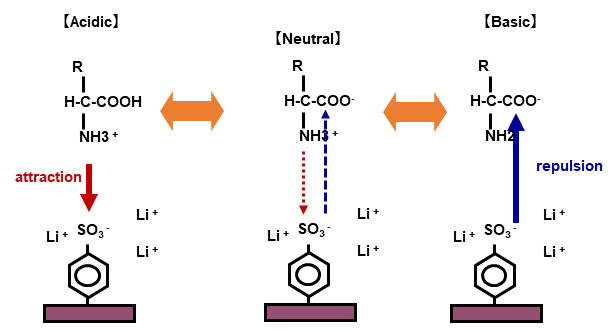
Fig. 5 Amino acid separation
The
cation exchange column has a high chemical strength and can be washed with
basic solutions. However, it doesn't have very high physical strength.
Sudden pressure fluctuations may cause degradation of the column, so you should
pay attention to the pressure applied to the column.
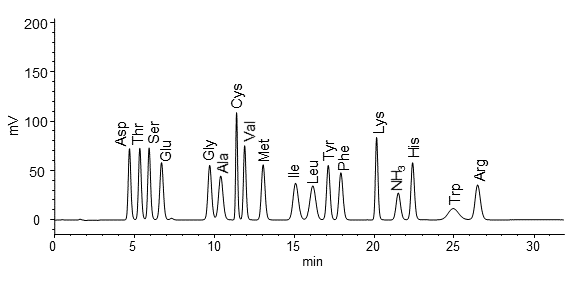
Fig. 6 Example of amino acids chromatogram
Table 2 Necessary elements for amino acid analysis buffer
|
Condition |
Chemicals |
|
pH |
Citric acid |
|
Ionic strength |
NaCl, LiCl |
|
buffer capacity |
Sodium citrate, Lithiun citrate |
Table 3 Other components of amino acid analysis buffer and purpose of addition
|
Reagents |
Porpose |
|
Ethanol |
separation of Thr-Ser |
|
Benzyl alcohol |
separation of Trp |
|
β-thiodiglycol |
anti-oxidation of sulfur-containing amino acids |
|
Brij-35 |
Pump pressure reduction |
|
Caprylic acid |
Anti-corruption |
The buffer solutions can be purchased locally. For the detail, you can ask local sales.
You can also prepare the buffer solutions according to the "Buffers preparation" section of the instruction manual (main unit). The pH value described in the instruction manual is a reference value and adjustment of pH is not necessary.
You have to use special grade reagents or reagents graded for amino acid analysis.
2-2. Derivatization of amino acids
There are two types of derivatization: pre-column and post-column. The post-column derivatization method adopted for the Hitachi High-speed Amino Acid Analyzer LA8080 has advantages such as less influence of contaminants and better reproducibility.
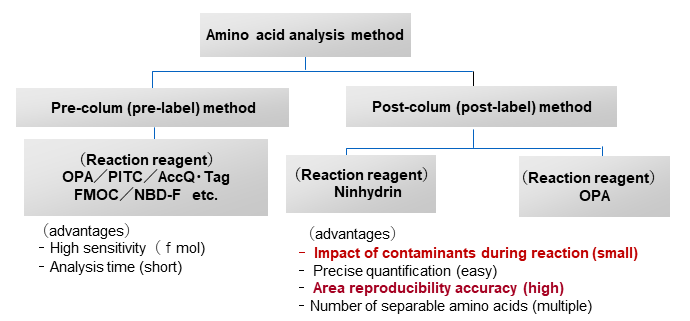
Fig. 7 Types of derivatization of amino acids
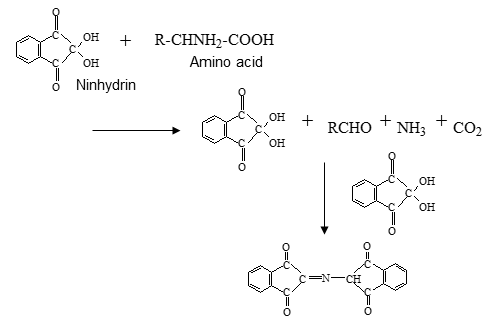
Fig. 8 Chemical reaction of amino acid and ninhydrin
Due to a ninhydrin reaction, a blue-violet substance (Ruhemann's purple) was produced and measured with the absorbance at 570 nm. Because proline and hydroxyproline produce yellow-red substances, they were measured with the absorbance at 440 nm.
3. Inside Front Doors
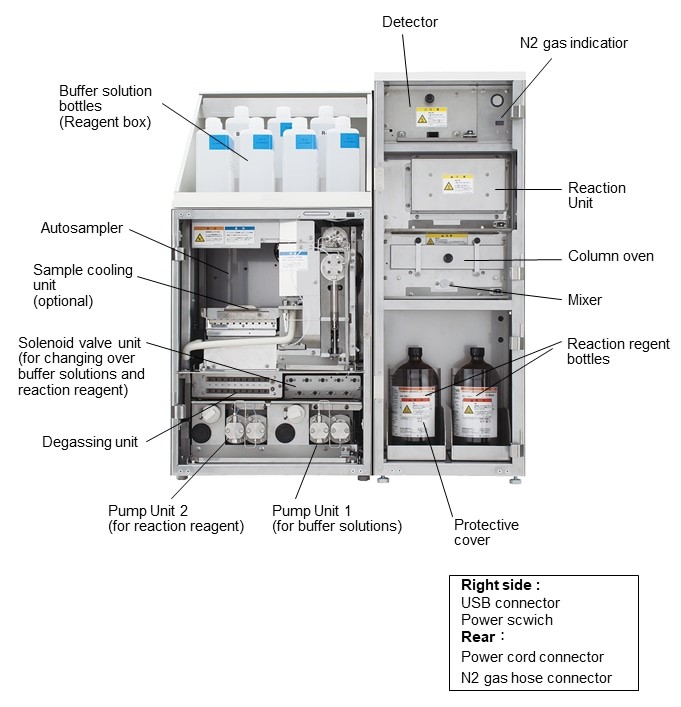
Cross-post from Hitachi High Tech
https://www.hitachi-hightech.com/global/products/science/tech/ana/lc/aaa_basic_course/
For more information on Hitachi Amino Acid Analyzer, please visit Hitachi High-Tech Science website
https://www.hitachi-hightech.com/global/product_detail/?pn=ana-la8080


 2606, 26/F., Tower 1, Ever Gain Plaza, 88 Container Port Road, Kwai Chung, N.T., Hong Kong
2606, 26/F., Tower 1, Ever Gain Plaza, 88 Container Port Road, Kwai Chung, N.T., Hong Kong +852-27519488 / WhatsApp/WeChat HK: +852-8491 7250
+852-27519488 / WhatsApp/WeChat HK: +852-8491 7250 techcomp@techcomp.com.hk
techcomp@techcomp.com.hk
 Sweep The Concern Us
Sweep The Concern Us